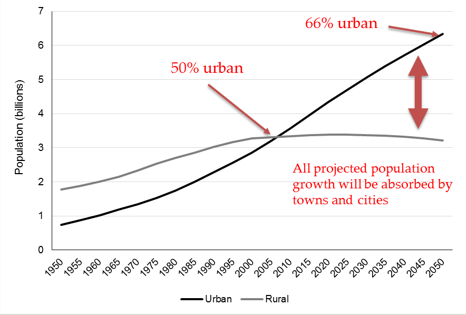
Figure 1. Rural and urban population trends, 1950-2050, Adapted from Fox, S. & Goodfellow, T. (2016) Cities and Development, Second Edition. Routledge.

Dr Sean Fox, Lecturer in Urban Geography and Global Development, University of Bristol
Sustainable Development Goal 11 outlines a global ambition to ‘make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable’. It is arguably one of the most important of the 17 recently agreed Goals, but we’re unlikely to reach it in most parts of the world by 2030.
The importance of Goal 11 stems from global demographic trends. As Figure 1 illustrates, over 50% of the world’s population already lives in towns and cities, and that percentage is set to rise to 66% by 2050. In fact, nearly all projected population growth between now and 2050 is expected to be absorbed in towns and cities, and the vast majority of this growth will happen in Africa and Asia (see Figure 2).
These trends mean that when it comes to eliminating poverty and hunger, improving health and education services, ensuring universal access to clean water and adequate sanitation, promoting economic growth with decent employment opportunities, and creating ‘responsible consumption and production patterns’ (and achieving many other goals) urban centres are on the front line by default. Continue reading

